As the world faces significant climate challenges, the pursuit of sustainable energy has never been more critical. Innovative technologies and scientific advancements are paving the way for a future driven by renewable energy sources. The latest research indicates that harnessing solar, wind, and other renewable energy will dramatically reduce reliance on fossil fuels while also driving economic growth.
Emerging solutions like energy storage systems and smart grids are enhancing the efficiency and accessibility of sustainable energy. Scientists are discovering new materials and methods that promise to revolutionize how energy is generated and stored, making it possible for communities worldwide to transition more effectively to cleaner sources.
The interplay between technology and renewable energy is changing the landscape of energy production. With ongoing research, it is evident that sustainable energy is not just a goal; it is becoming a practical reality that promises a healthier planet and sustainable future.
Current Landscape of Sustainable Energy
The sustainable energy landscape is evolving rapidly. It encompasses renewable energy sources, the ongoing competition with fossil fuels, and the pressing issues of greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
Overview of Renewable Sources
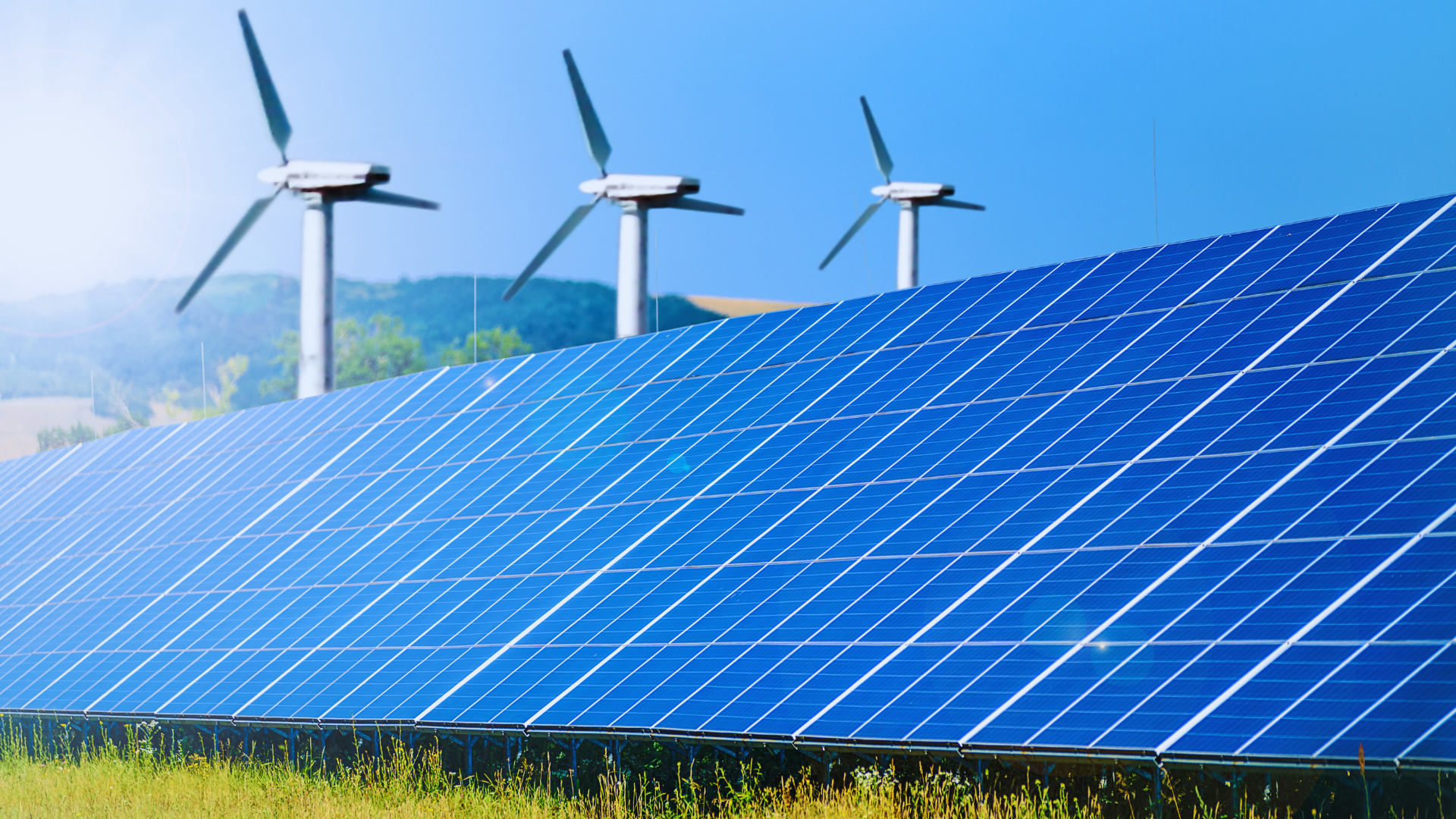
Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal play a crucial role in decreasing dependence on fossil fuels. In 2023, renewables contributed over 29% of global electricity generation.
- Solar Energy: Photovoltaics and concentrated solar power systems have seen significant adoption, with costs dropping sharply.
- Wind Energy: Both onshore and offshore wind farms are expanding, contributing to substantial energy production.
- Hydropower: Remains a significant source but faces challenges regarding ecological impacts and sustainability.
These renewable sources provide cleaner alternatives that help mitigate climate change and pollution.
Fossil Fuels Versus Clean Energy
Fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, still dominate global energy production. However, their use leads to significant greenhouse gas emissions.
- Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Fossil fuel combustion accounts for about 75% of total CO2 emissions globally.
- Energy Transition: Many countries are investing in transitioning from fossil fuels to sustainable alternatives.
This competition highlights the urgency for cleaner energy solutions, balancing economic and environmental needs.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Global Warming
Greenhouse gas emissions are a critical factor in global warming, primarily driven by human activity. Combustion of fossil fuels generates high levels of CO2, contributing to rising temperatures.
- Impact on Climate Change: Increased emissions lead to extreme weather, rising sea levels, and ecosystem disruption.
- Mitigation Efforts: Countries are implementing policies to reduce emissions, promoting renewable energy adoption, and energy efficiency.
Addressing these challenges through sustainable energy solutions is essential for future climate stability.
Scientific Innovations Driving the Future
Recent advancements in energy technologies are laying the groundwork for a sustainable future. Key innovations include developments in energy storage, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, breakthroughs in carbon capture, and the application of synthetic biology for producing renewable fuels.
Advanced Energy Storage Technologies
Energy storage is pivotal for managing supply and demand in renewable energy systems. Solid-state batteries represent a significant leap forward. They offer enhanced energy density, safety, and longevity compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
These batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, reducing the risk of leaks and fires. Research has shown that they could potentially provide up to three times the energy storage capacity.
Other innovations include flywheel energy storage and pumped hydro storage. These technologies can harness excess energy and release it during peak demand, increasing grid reliability and efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming how energy systems are managed. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI can optimize energy consumption and identify patterns in renewable energy generation.
These technologies help in predictive maintenance for energy systems, reducing operational costs and downtime. They also enhance grid management by forecasting energy needs and adjusting supply accordingly.
Moreover, AI-driven algorithms are being developed to optimize the design and operation of renewable energy systems, such as wind and solar farms. This leads to improved efficiency and reduced energy waste.
Breakthroughs in Carbon Capture
Carbon capture technology plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Significant scientific advancements have enhanced the efficiency of capturing CO2 from industrial processes and the atmosphere.
Innovative materials such as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are being explored for their ability to absorb carbon effectively. These materials can capture CO2 at lower energy costs, making the process more economically viable.
Some facilities now utilize direct air capture technology, which can remove CO2 from ambient air. This approach not only mitigates emissions but also enables carbon recycling to produce useful products.
Synthetic Biology for Renewable Fuels
Synthetic biology is paving the way for the creation of renewable fuels from organic materials. Researchers are engineering microorganisms to convert sugars and lipids into biofuels, creating a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
These engineered microbes can produce fuels such as ethanol and biodiesel directly from plant waste. Innovations in this space are also contributing to the development of renewable diesel, a cleaner-burning fuel made from renewable feedstocks that can fully replace conventional diesel without engine modifications. This progress not only reduces reliance on traditional fossil fuel sources but also helps to minimize waste.
As renewable fuel technologies move from the laboratory to real-world applications, fuel distributors are playing a key role in adoption. Companies like Red Triangle Oil Co, which supplies renewable diesel and other fuel solutions, demonstrate how advanced biofuel technologies are being integrated into existing fuel delivery systems to support cleaner energy use across commercial, agricultural, and industrial sectors. Continued research in synthetic biology is likely to enhance the efficiency of these processes, making renewable fuels more competitively priced. As technologies evolve, they hold promise for significant contributions to a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape.
Emerging Solutions and Technologies
Advancements in sustainable energy are transforming how the world approaches energy production and consumption. Innovations in various sectors promise to enhance efficiency, reduce emissions, and meet rising energy demands.
Innovations in Wind and Solar Power
Recent developments in wind and solar technologies are driving significant improvements. Next-generation wind turbines feature larger blades and advanced materials, enhancing energy capture efficiency. Floating wind farms are also making offshore locations more accessible, increasing overall capacity.
On the solar side, bifacial solar panels are gaining traction. These panels can capture sunlight on both sides, boosting efficiency. Advances in solar tracking systems allow panels to follow the sun’s path, further increasing energy generation. Combining these technologies helps reduce costs and increase the viability of solar power. For homeowners looking to combine panel technology with local installation, battery backup, and help navigating incentives, many rely on trusted solar companies in pennsylvania (or elsewhere) that specialize in residential systems and storage solutions.
Green Hydrogen and Hydrogen Fuel Developments
Green hydrogen is gaining attention as a clean alternative to fossil fuels. Produced via electrolysis powered by renewable energy, it offers a zero-emission option for energy storage and transport. Various countries are investing in hydrogen production facilities, targeting significant reductions in production costs.
The transportation sector is also exploring hydrogen fuel cells for electric vehicles (EVs). Fuel cell technology provides longer ranges and quicker refueling compared to battery-electric options. Additionally, this technology can help decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors, such as industrial processes and shipping.
Geothermal Energy and Enhanced Geothermal Systems
Geothermal energy is a reliable, low-emission resource that utilizes heat from the Earth. Recent advancements in enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) are expanding its potential. EGS involves injecting water into hot rock formations to generate steam for power production.
This technology allows for geothermal power generation in areas previously considered unsuitable. Countries harnessing geothermal resources are finding it a stable source amid fluctuating energy demands. Combined with advancements in drilling technologies, EGS has the potential to make geothermal energy a cornerstone of renewable energy strategies.
Electric Vehicles and Grid Integration
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is reshaping energy consumption patterns. As more consumers adopt EVs, the need for efficient grid integration becomes apparent. Smart grids are incorporating real-time data analytics to optimize energy distribution and storage.
Charging infrastructure is also expanding, with microgrids ensuring energy supply at local levels. Additionally, vehicle-to-grid technologies allow EVs to return energy to the grid during peak demand, enhancing overall grid resilience. This symbiosis between EVs and the electricity grid signals a shift towards a more sustainable, interconnected energy system.
Transitional Fuels and Their Role in the Energy Shift
Transitional fuels play an important part in supporting the global shift from conventional fossil fuels to fully renewable systems. They provide a practical bridge for sectors that cannot yet rely exclusively on solar, wind, or other clean energy sources, helping reduce emissions without requiring complete infrastructure changes.
Propane is one of the most effective transitional fuels, burning cleaner than gasoline, diesel, and coal while producing lower greenhouse gas emissions. It delivers reliable performance not only for heating, backup power, and industrial processes, but also for a wide range of home uses such as cooking, water heating, and whole-house generators. Its versatility and availability make it an efficient option for households, businesses, and communities seeking immediate reductions in their carbon footprint.
Organizations and homeowners can turn to a trusted propane company to ensure consistent supply of cleaner-burning propane. With dependable delivery and support, these providers help in transitioning smoothly toward sustainable energy strategies while longer-term renewable solutions continue to expand.
Pathways Toward a Sustainable Future
A sustainable future involves a multifaceted approach that encompasses energy security, carbon dioxide emissions reduction, and the development of resilient energy solutions. These aspects are critical for addressing climate change and ensuring a stable energy landscape.
Energy Security and Policy Implications
Energy security is vital for national economies and global stability. Policies promoting renewable energy can enhance energy independence, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Strategic investments in infrastructure, such as smart grids and energy storage systems, bolster energy security.
Governments play a crucial role in establishing regulations that encourage sustainable energy production. Incentives for renewable energy technologies, alongside strict emissions targets, are key components of effective energy policy. International cooperation can further bolster energy security through resource-sharing agreements and collaborative innovation.
Reducing Carbon Dioxide Emissions
Reducing carbon dioxide emissions is essential for combating climate change. Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power significantly lowers emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels.
That said, for many households, these solutions may not fully meet energy needs due to factors such as cost, availability, infrastructure limitations, or inconsistent energy supply. In such cases, utilizing lower-carbon alternatives can often help bridge the gap.
Propane, for instance, tends to burn cleaner than many conventional fuels and can reduce carbon emissions when used for heating, cooking, and other household applications. Therefore, by enlisting the services of a reputable provider like TJ Propane, homeowners can adopt more reliable and comparatively carbon-efficient energy solutions while continuing to work toward broader sustainability goals.
Moreover, efforts to improve energy efficiency in buildings and transportation also mitigate emissions. Implementing advanced technologies, such as carbon capture and storage (CCS), has the potential to reduce emissions from existing power plants. Local initiatives that promote public transportation and electric vehicles contribute positively to lowering overall carbon footprints.
Building Resilient Sustainable Energy Solutions
Resilient, sustainable energy solutions are necessary to adapt to changing environmental conditions. This includes developing decentralized energy systems that can withstand disruptions from natural disasters or adverse events.
Investments in innovative technologies, like microgrids and energy storage solutions, enhance resilience. Community involvement and education play significant roles in promoting acceptance and usage of sustainable practices.
Utilizing diverse energy portfolios is also essential. Combining various renewable sources can ensure consistent energy availability while minimizing vulnerabilities associated with single-source dependencies.