Throughout history, the realms of science and art have often intersected in profound ways, shaping culture and innovation. Key figures have blended these disciplines, creating a rich tapestry of ideas and expressions that reflect both human emotion and scientific discovery. The interplay between science and art reveals how creativity can inform and enhance scientific understanding, while empirical inquiry can inspire artistic expression.
From the meticulous studies of human anatomy by Renaissance artists to the use of color theory in scientific exploration, the collaboration between these fields has led to groundbreaking advancements. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci exemplified this connection, using scientific principles to enhance the realism of their work. This synthesis has not only fostered growth in individual disciplines but also prompted societal shifts in perspective.
As society progresses, this relationship continues to evolve, influencing contemporary practices in ways that challenge traditional boundaries. Understanding how science and art influence each other provides insights into the creative processes that drive human achievement.
Historical Foundations of the Link Between Science and Art
Throughout history, the relationship between science and art has manifested in various ways, reflecting a mutual influence. This section explores key elements such as Renaissance innovations, prominent figures like Leonardo da Vinci and Rembrandt, and their focus on observation and anatomy, all contributing to the foundational link between these two disciplines.
Renaissance Innovations and the Merging of Disciplines
The Renaissance marked a pivotal point where art and science began to merge significantly. This era saw artists and scientists collaborating, utilizing advancements in materials and methods. The invention of linear perspective allowed artists to create realistic spatial representations, while studies in anatomy provided a deeper understanding of human form.
Significant developments included the use of oil paints, which offered a wider range of colors and textures. Artists such as Albrecht Dürer systematically studied nature, documenting their findings through sketches and paintings. This blending of approaches fostered a culture of exploration that influenced subsequent artistic movements.
Master’s Bridging Art and Science: Leonardo da Vinci and Rembrandt
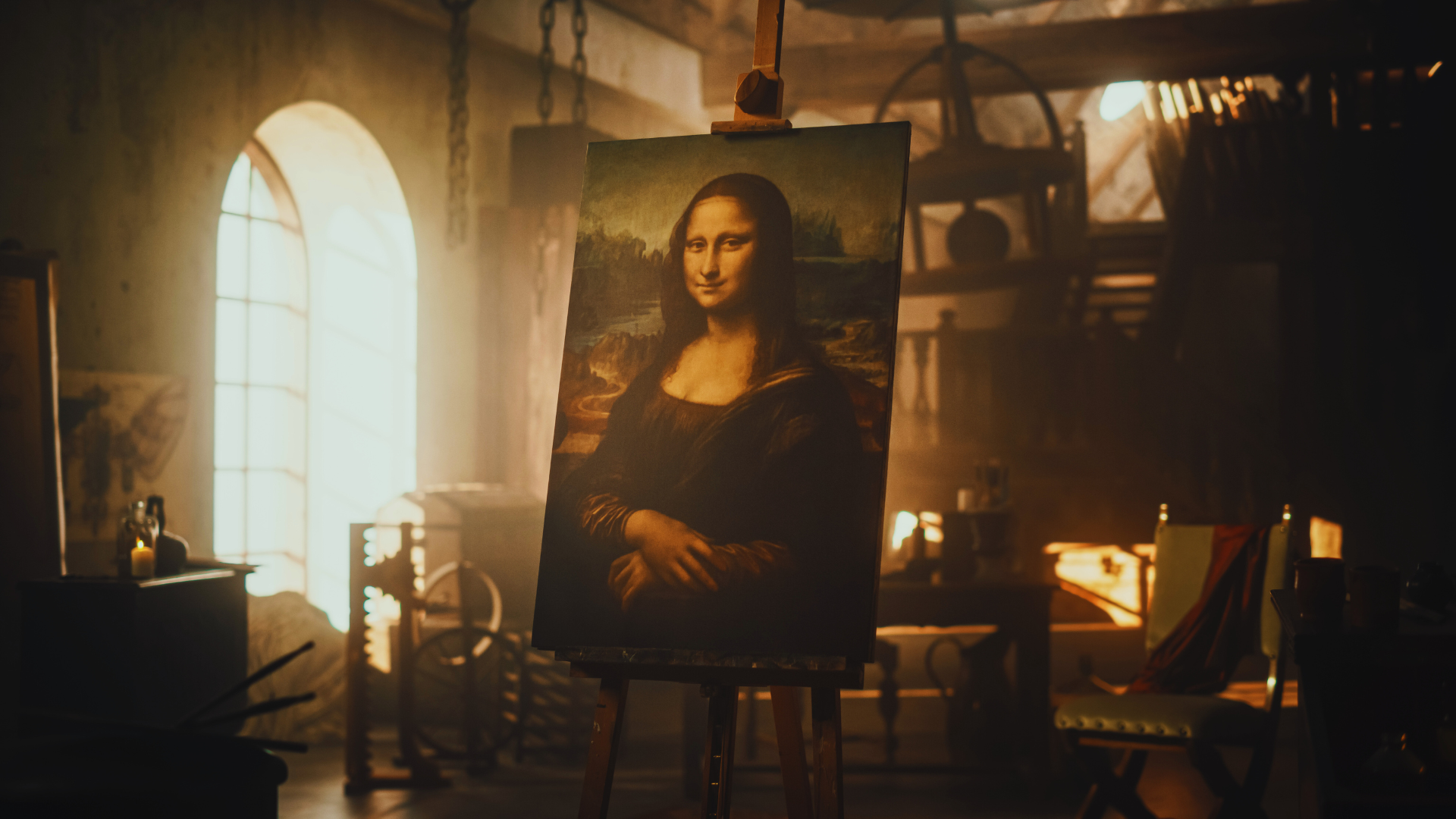
Leonardo da Vinci epitomized the integration of art and science through his extensive studies in anatomy and engineering. His sketches, such as those for flying machines and the human body, represent a unique fusion of artistic vision and scientific inquiry. This approach is evident in works like the “Mona Lisa” and the “Vitruvian Man.”
Rembrandt also contributed to this dialogue but focused more on human emotion and anatomy in his paintings. His work “Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp” illustrates the relationship between artist and scientist, showcasing the human body with precision while capturing the essence of the moment. Both artists exemplified how detailed observation could enhance the creative process.
Observation, Anatomy, and the Natural World in Classical Works
Observation laid the groundwork for both scientific inquiry and artistic representation during the classical periods. Detailed studies of the natural world motivated artists to depict plants, animals, and landscapes with accuracy. This commitment to realism can be seen in the works of artists who sought to understand and represent their surroundings faithfully.
Human anatomy became a focal point for many during the Renaissance, prompting artists to conduct dissections to gain deeper insights. Their anatomical studies not only improved artistic technique but also contributed to medical knowledge. As a result, the artistic interpretations of the human form became increasingly sophisticated, bridging the gaps between scientific understanding and artistic expression.
Interconnected Methods and Shared Concepts
The relationship between science and art is evident through their shared methods and concepts. Both domains employ various techniques to visualize and communicate complex ideas, which enhance understanding and appreciation.
Geometry, Visualization, and Techniques of Representation
Geometry plays a crucial role in both art and science. In art, artists utilize geometric principles to create balanced compositions and accurate depictions of forms. Techniques like perspective rely on geometry to simulate depth and proportion, enabling realistic representation in paintings and sculptures.
In science, geometry aids in the visualization of structures and patterns. For example, the geometric shapes found in crystal formations help scientists understand molecular arrangements. The mathematical precision in both realms facilitates clear communication of ideas and concepts.
Scientific Illustration and Data Visualization
Scientific illustration serves as a bridge between artistic representation and scientific accuracy. These illustrations are meticulously created to depict biological specimens, celestial bodies, and anatomical structures. Artists use techniques such as shading and color to add depth and clarity, ensuring that viewers can comprehend complex subjects.
Data visualization has emerged as a significant tool in presenting scientific findings. Graphs, charts, and infographics transform raw data into formats that are easily interpretable. By employing artistic principles, these visualizations enhance communication and promote a better understanding of scientific research.
Technological Advancements: Microscope, Telescope, and Photography
Technological advancements have significantly contributed to the intersection of art and science. The microscope allows scientists to explore the minutiae of biological structures, revealing details previously invisible. Artists have adapted these findings to inform their work, enriching their representations of microscopic life.
The telescope expanded our understanding of the cosmos, enabling artists to depict celestial phenomena with greater accuracy. Photography revolutionized both fields by providing a new medium for capturing reality. It further allowed scientists and artists to document their observations, merging artistic expression with scientific inquiry.
Color Theory, Human Form, and the Study of Anatomy
Color theory is essential in both artistic and scientific contexts. Artists explore color relationships to evoke emotions and create visual harmony in their work. Understanding color interactions is crucial for achieving desired effects in paintings and drawings.
In science, color theory aids in the study of human anatomy. Accurate representation of the human form requires a deep understanding of skin tones, blood flow, and anatomical structures. Artists trained in anatomy utilize this knowledge for realistic portrayals, while scientists benefit from detailed illustrations that enhance their understanding of biological functions.
Contemporary Perspectives: Symbiosis and Innovation
The intersection of science and art has given rise to vibrant movements and innovative practices. Contemporary artists draw inspiration from scientific concepts, leading to groundbreaking works that challenge traditional boundaries. This dynamic relationship fosters creativity and a deeper understanding of both fields.
Art Movements Inspired by Science
Art movements like cubism and pointillism have roots in scientific theories. Cubism, championed by Pablo Picasso, transformed perspective and form, echoing developments in visual perception. Artists deconstructed objects to explore multiple viewpoints simultaneously.
Pointillism, developed by Georges Seurat, utilized color theory and optics, applying scientific principles to create depth and light. These movements illustrate how artists engage with scientific concepts, highlighting the symbiotic nature of art and science throughout history.
Digital Art, BioArt, and Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Digital art has revolutionized artistic expression, allowing for new forms of creativity. Artists like Aaron Koblin utilize data visualization to manifest complex information aesthetically. This blending of art and technology results in immersive experiences that engage audiences uniquely.
BioArt represents another frontier, as artists incorporate living organisms, manipulating biological processes. This interdisciplinary collaboration raises ethical questions and prompts dialogue about life and technology, demonstrating how scientific inquiry inspires innovative artistic practices.
Modern Visualization: Fractals, Chaos Theory, and Data
Fractals and chaos theory provide mathematical foundations that resonate with contemporary art. Artists apply these concepts to produce intricate visual patterns, representing complexity in nature and systems. Works inspired by fractals reflect natural phenomena, merging mathematics with aesthetics.
Data visualization has emerged as a critical tool for artists to represent information. Using algorithms, artists create compelling narratives from raw data. This approach not only enhances comprehension but also invites viewers to explore connections between the numerical and the visual, emphasizing the ongoing dialogue between science and art.
Broader Cultural Impact and Societal Change
The intersection of art and science has significantly influenced human creativity and society at large. This relationship has facilitated the communication of complex ideas and acted as a catalyst for social and environmental change.
Human Creativity and the Drive for Discovery
Human creativity thrives at the crossroads of art and science. Artists and scientists alike engage in exploration, pushing the boundaries of human understanding. Creative expression, whether through visual art or scientific theory, fosters innovation.
Historical figures like Leonardo da Vinci exemplified this synergy. His anatomical sketches revealed insights into the human body, bridging artistic vision with scientific inquiry. This interplay encourages a culture of discovery, prompting future generations to explore and create.
Art, Science, and the Communication of Complex Ideas
Art and science collaborate to convey intricate concepts effectively. Scientific theories, like Einstein’s theory of relativity, often rely on visual representations to make complex ideas more accessible. Here, artistic interpretation serves as a tool for communication.
Visual art can translate natural phenomena into experiences that resonate emotionally. For example, Olafur Eliasson’s installations often address climate change through immersive experiences, prompting viewers to reflect on their relationship with the environment.
Catalysts for Social and Environmental Change
The blend of art and science plays a pivotal role in advocating for social and environmental change. Artistic expression raises awareness about pressing issues, from climate change to social justice. Events like exhibitions or installations can mobilize communities around critical causes.
Furthermore, collaborative projects between scientists and artists can drive significant dialogue. Initiatives that creatively visualize data on climate change catapult scientific understanding into public discourse, fostering activism. This symbiotic relationship underscores how intertwined creativity and discovery fuel societal transformation.